First, what is a middle mile network?
Middle Mile Network is an industry term that describes the network infrastructure that connects “last mile” (i.e., local) networks to other network service providers, major telecommunications carriers, and the greater internet. It does not typically connect the majority of end-users.
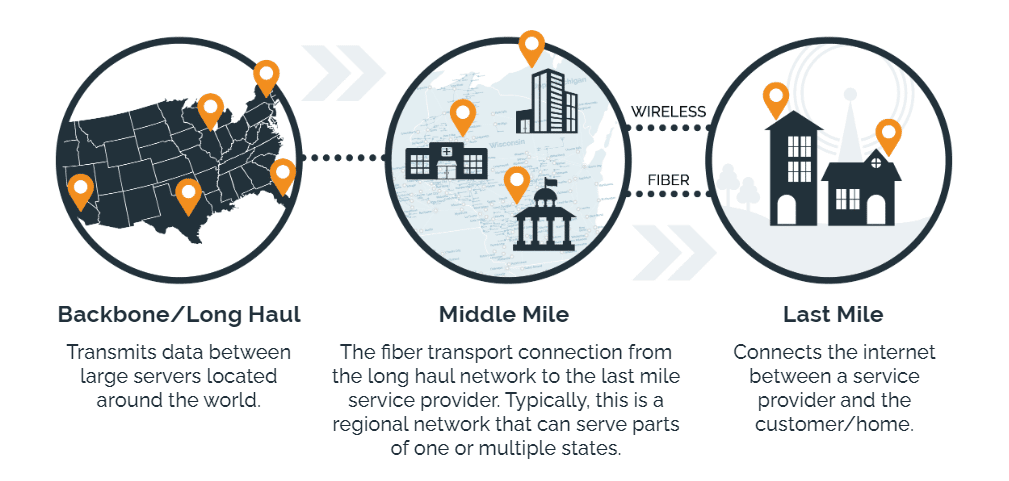
Why is there a need for a middle mile network?
In many areas throughout the Midwest, there is no middle mile network located close enough to connect last mile infrastructure. Or the only nearby middle mile is privately owned by a large Internet Service Provider (ISP) who can selectively determine the business criteria to serve the area.
According to FCC data, nearly 40 percent of people in the U.S. have only one Internet Service Provider in their area to choose from. In many rural Midwestern areas, the percentage is even higher. When one major ISP owns the middle mile of an area, they tend to either charge above market rate prices for other ISPs to connect, or they don’t allow them to connect at all. It can be very difficult for other ISPs to connect to a middle mile network if it requires negotiating costs with their direct competitor.
What are the benefits of a middle mile network?
Developing middle mile infrastructure can provide a solution to expensive network connections by expanding internet networks closer to unserved and underserved communities. Middle mile networks offer equal opportunity for ISPs to link cost-effectively to last mile infrastructure. This can connect more people to high-speed internet while also driving down prices by increasing competition among local ISPs. It also enables new technologies, such as Internet of Things (IoT) to be used in manufacturing, robotics, and precision farming. This allows for more efficient use of energy and other critical environmental resources.
In addition to potentially helping narrow the digital divide, middle mile infrastructure can:
- Provide backup options for networks if one connection pathway fails.
- Support regional economic growth by connecting people to opportunities, jobs, and education.
- Attract and retain businesses; and ultimately enable many underserved areas to be better positioned for potential projects and programs.
Advantages of WIN Technology’s middle mile network
- Designed for the Future: The WIN fiber network is easily scalable, ready to enable new technologies, and includes sophisticated network monitoring, certified network engineer management, and automatic route failover in case a fiber cut does occur.
- Climate Resistant: Due to its buried conduit design, our fiber is resilient to elements like wind, lightning, tornadoes, tree falls, and any human intervention that would occur above ground.
- Monitored, Operated and Maintained 24/7: Our Network Operations Center (NOC) is staffed locally and trained in all the services and systems we support with the goal of “one call resolution” to ensure the network is fully supported.
- Easy Access: We employ a flexible fiber access policy that permits the creation of vaults and meet-me locations for last mile providers. WIN’s middle mile is also connected to two wholly owned data centers and has presence in 23 data centers and 150 POP locations across the Midwest.
- More Than Just Fiber: Our 20,000+ miles of fiber optic network support life-enhancing technology services, enables remote workforces, and provides access to public safety, education, healthcare, e-commerce, global markets, disability services and entertainment.
Ready to learn more?
If you have questions or want to learn more about the middle mile network, contact us for a no-obligation consultation.
